Blocking cardiac NET formation by HMGB1 neutralization
Blocking cardiac NET formation by HMGB1 neutralization
|
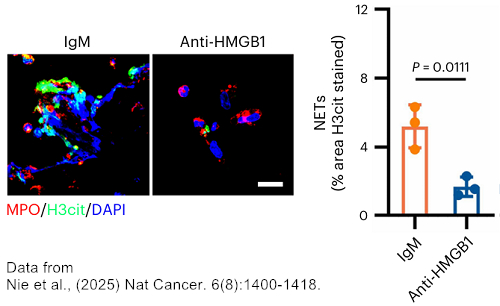
arigo is proud to announce that our HMGB1 Neutralizing antibody (ARG66714) was used to block cardiac NET formation in doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity, with the findings published in Nat Cancer. 6(8):1400-1418. (IF 28.5) Nie et al. investigated the mechanism of cardiotoxicity caused by chemotherapeutic agent doxorubicin (DOX). The authors found that DOX induces HMGB1 release from cardiomyocytes, which subsequently promotes the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), leading to cardiac dysfunction. Our HMGB1 Neutralizing antibody was used to demonstrate that targeting HMGB1 significantly reduced NET formation. HMGB1 plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of NET-associated disorders. arigo offers comprehensive HMGB1 products and neutrophil research tools to support scientific exploration of HMGB1-dependent NET formation.
|
|
|
HMGB1 Neutralizing antibody [SQab20175] (ARG66714)
|
● HMGB1-specific Mouse mAb (Recommended control: ARG20592) |
 |
|
|
more HMGB1 products
 |
● Quantification by HMGB1 ELISA kits ● Stimulation by HMGB1 active protein ● Blocking by HMGB1 Neutralizing antibody ● Detection by HMGB1 antibodies |
