ARG44057
anti-CD158a + CD158g CD158h antibody [HP-MA4] (PE-Cyanine 7)
anti-CD158a + CD158g CD158h antibody [HP-MA4] (PE-Cyanine 7) for Flow cytometry and Human
概述
| 产品描述 | PE-Cyanine 7-conjugated Mouse Monoclonal antibody recognizes CD158a + CD158g CD158h |
|---|---|
| 反应物种 | Hu |
| 应用 | FACS |
| 特异性 | The mouse monoclonal antibody HP-MA4 recognizes an extracellular epitope of CD158 isoforms KIR2DL1 (CD158a), KIR2DS5 (CD158g), KIR2DS1 (CD158h), and KIR2DS3. It does not recognize the isoforms CD158b1,d,f,i,j. |
| 宿主 | Mouse |
| 克隆 | Monoclonal |
| 克隆号 | HP-MA4 |
| 同位型 | IgG2a |
| 靶点名称 | CD158a + CD158g+ CD158h |
| 抗原物种 | Human |
| 抗原 | Human NK cell line LB2 |
| 偶联标记 | PE-Cyanine 7 |
| 別名 | KIR2DL1; Killer Cell Immunoglobulin Like Receptor, Two Ig Domains And Long Cytoplasmic Tail 1; CD158A ; KIR2DS5; Killer Cell Immunoglobulin Like Receptor, Two Ig Domains And Short Cytoplasmic Tail 5; CD158G; KIR2DS1; Killer Cell Immunoglobulin Like Receptor, Two Ig Domains And Short Cytoplasmic Tail 1; CD158H |
应用说明
| 应用建议 |
|
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 应用说明 | * The dilutions indicate recommended starting dilutions and the optimal dilutions or concentrations should be determined by the scientist. |
属性
| 形式 | Liquid |
|---|---|
| 缓冲液 | PBS (pH 7.4) and 15 mM Sodium azide |
| 抗菌剂 | 15 mM Sodium azide |
| 存放说明 | Aliquot and store in the dark at 2-8°C. Keep protected from prolonged exposure to light. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. Suggest spin the vial prior to opening. The antibody solution should be gently mixed before use. |
| 注意事项 | For laboratory research only, not for drug, diagnostic or other use. |
生物信息
| 基因名称 | KIR2DL1; KIR2DS5; KIR2DS1 |
|---|---|
| 全名 | Killer Cell Immunoglobulin Like Receptor, Two Ig Domains And Long Cytoplasmic Tail 1; Killer Cell Immunoglobulin Like Receptor, Two Ig Domains And Short Cytoplasmic Tail 5; Killer Cell Immunoglobulin Like Receptor, Two Ig Domains And Short Cytoplasmic Tail 1 |
| 背景介绍 | Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several "framework" genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. KIR proteins with the long cytoplasmic domain transduce inhibitory signals upon ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), while KIR proteins with the short cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM motif and instead associate with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules; thus, KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulation of the immune response. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several "framework" genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. KIR proteins with the long cytoplasmic domain transduce inhibitory signals upon ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), while KIR proteins with the short cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM motif and instead associate with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules; thus, KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulation of the immune response. Killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIRs) are transmembrane glycoproteins expressed by natural killer cells and subsets of T cells. The KIR genes are polymorphic and highly homologous and they are found in a cluster on chromosome 19q13.4 within the 1 Mb leukocyte receptor complex (LRC). The gene content of the KIR gene cluster varies among haplotypes, although several "framework" genes are found in all haplotypes (KIR3DL3, KIR3DP1, KIR3DL4, KIR3DL2). The KIR proteins are classified by the number of extracellular immunoglobulin domains (2D or 3D) and by whether they have a long (L) or short (S) cytoplasmic domain. KIR proteins with the long cytoplasmic domain transduce inhibitory signals upon ligand binding via an immune tyrosine-based inhibitory motif (ITIM), while KIR proteins with the short cytoplasmic domain lack the ITIM motif and instead associate with the TYRO protein tyrosine kinase binding protein to transduce activating signals. The ligands for several KIR proteins are subsets of HLA class I molecules; thus, KIR proteins are thought to play an important role in regulation of the immune response. |
| 生物功能 | Receptor on natural killer (NK) cells for some HLA-C alleles such as w4 and w6. Inhibits the activity of NK cells thus preventing cell lysis. Receptor functions are attenuated even lost in some alleles, such as KIR2DS5*002 reprensented in this entry. Receptor on natural killer (NK) cells for some HLA-C alleles such as w6. Does not inhibit the activity of NK cells. |
| 细胞定位 | Cell membrane, Membrane |
| 翻译后修饰 | Disulfide bond, Glycoprotein |
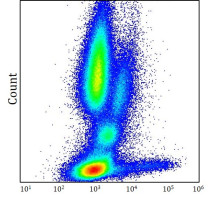
检测图片 (1) Click the Picture to Zoom In